LC 124 - Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum
Question
A path in a binary tree is a sequence of nodes where each pair of adjacent nodes in the sequence has an edge connecting them. A node can only appear in the sequence at most once. Note that the path does not need to pass through the root.
The path sum of a path is the sum of the node’s values in the path.
Given the root of a binary tree, return the maximum path sum of any non-empty path.
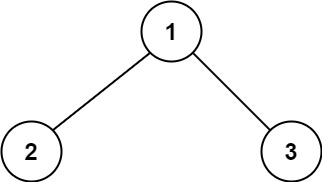
Example 1:
1
2
Input: root = [1,2,3]
Output: 6 **Explanation:** The optimal path is 2 -> 1 -> 3 with a path sum of 2 + 1 + 3 = 6.
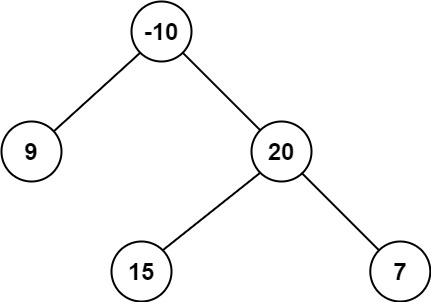
Example 2:
1
2
Input: root = [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 42 **Explanation:** The optimal path is 15 -> 20 -> 7 with a path sum of 15 + 20 + 7 = 42.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 3 * 104]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
Links
Question here and solution here
Solution
concept
There are two possibilities when traverse the graph using DFS, at each node:
- the max sum path comes from either the left or the right child path: we have to choose the max one and return to the parent
- the max sum path actually pass the current node, this means the max path is left path -> current node -> right path, so we have to keep a variables to be updated in case this case appear
Note that in the code, the left_max = max(left_max, 0) right_max = max(right_max, 0) has to be made first before calculating the include_cur because we do not want to add negatives into the current path calculation This also means that whenever we choose 0, that child path (either left or right) is not being considered, that is why we only need to update include_cur = left_max + right_max + node.val, this line already includes the case where only one path is chosen.
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def maxPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
self.ans = root.val
def dfs(node):
if not node:
return 0
left_max = dfs(node.left)
right_max = dfs(node.right)
# need to do this first, else the -ve will be added into include_cur
left_max = max(left_max, 0)
right_max = max(right_max, 0)
# path that includes the current node: i.e the path split
include_cur = left_max + right_max + node.val
self.ans = max(self.ans, include_cur)
# return path that is not split: i.e. choose one from the child path
return node.val + max(right_max, left_max)
dfs(root)
return self.ans
Complexity
time: $O(n)$
space: $O(n)$