LC 133 - Clone Graph
Question
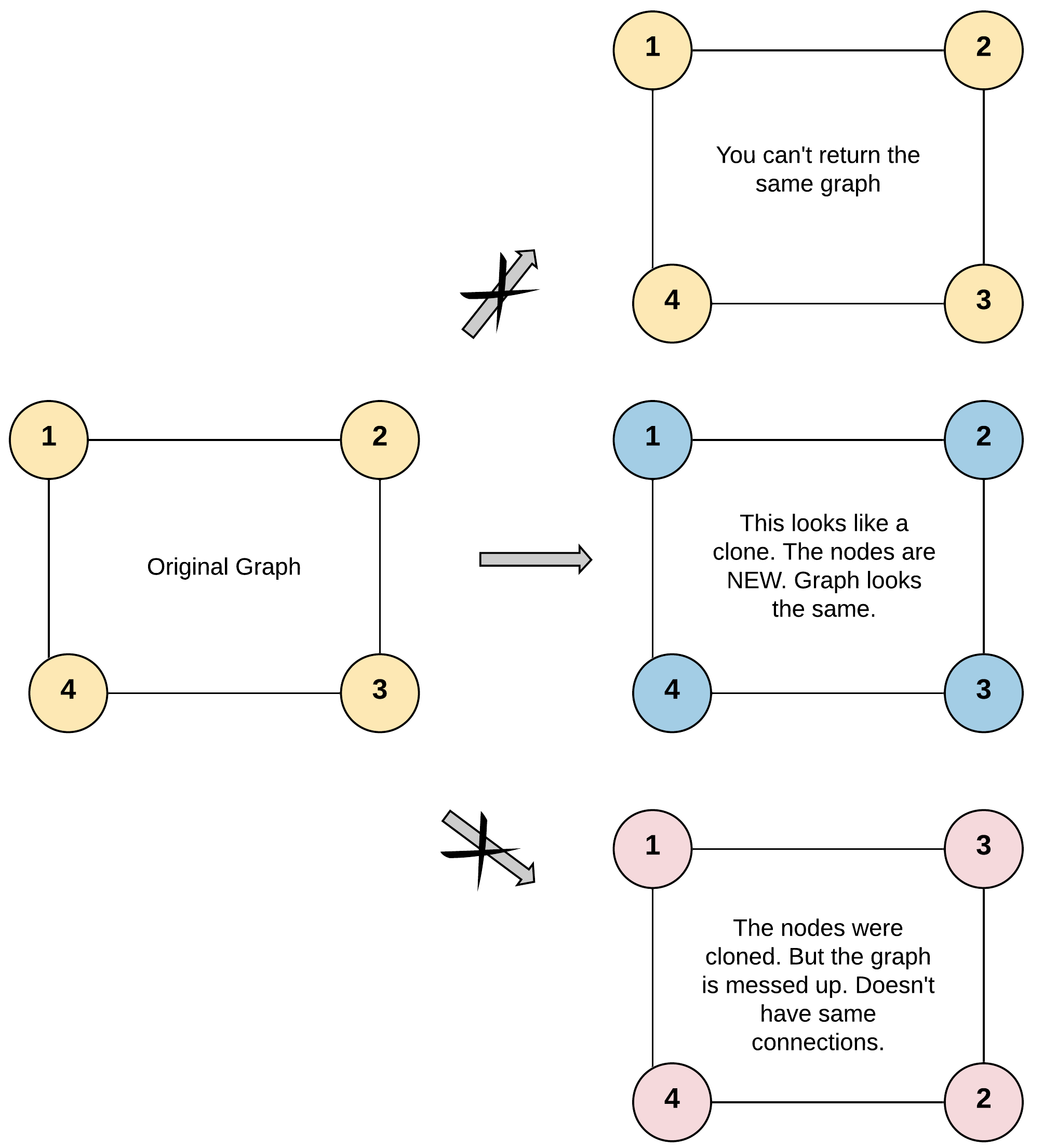
Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph.
Return a deep copy (clone) of the graph.
Each node in the graph contains a value (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
1
2
3
4
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> neighbors;
}
Test case format:
For simplicity, each node’s value is the same as the node’s index (1-indexed). For example, the first node with val == 1, the second node with val == 2, and so on. The graph is represented in the test case using an adjacency list.
An adjacency list is a collection of unordered lists used to represent a finite graph. Each list describes the set of neighbors of a node in the graph.
The given node will always be the first node with val = 1. You must return the copy of the given node as a reference to the cloned graph.
Example 1:
1
2
Input: adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]
Output: [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]
Explanation: There are 4 nodes in the graph. 1st node (val = 1)’s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4). 2nd node (val = 2)’s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3). 3rd node (val = 3)’s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4). 4th node (val = 4)’s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
Example 2:
1
2
Input: adjList = [[]]
Output: [[]] **Explanation:** Note that the input contains one empty list. The graph consists of only one node with val = 1 and it does not have any neighbors.
Example 3:
1
2
Input: adjList = []
Output: [] **Explanation:** This an empty graph, it does not have any nodes.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the graph is in the range
[0, 100]. 1 <= Node.val <= 100Node.valis unique for each node.- There are no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph.
- The Graph is connected and all nodes can be visited starting from the given node.
Links
Question here and solution here
Solution
concept
Use a hashmap to keep track the mapping from old node to new node. This hashmap has 2 purposes: 1) check if a node has been cloned in $O(1)$ 2) if cloned, we can retrieve and return the cloned node directly in $O(1)$ Please note the Python stores reference (pointer) and not snapshot, so old_to_new[node] = copy both points to the same address of the node, if we modify the node, all calling to the node can reflect that.
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val = 0, neighbors = None):
self.val = val
self.neighbors = neighbors if neighbors is not None else []
"""
from typing import Optional
class Solution:
"""
DFS solution
"""
def cloneGraph(self, node: Optional['Node']) -> Optional['Node']:
old_to_new = {} # old node to new node
def dfs(node):
if node in old_to_new:
return old_to_new[node]
copy = Node() # the starting point
copy.val = node.val
old_to_new[node] = copy # we store the pointer to the incomplete node first
for nei in node.neighbors:
copy.neighbors.append(dfs(nei))
return copy
return dfs(node) if node else None
class Solution:
"""
BFS solution
"""
def cloneGraph(self, node: Optional['Node']) -> Optional['Node']:
old_to_new = {} # old node to new node
def bfs(node):
copy = Node(node.val) # the starting point
old_to_new[node] = copy
q = deque([node])
while q:
old_curr = q.popleft()
for nei in old_curr.neighbors:
if nei not in old_to_new:
old_to_new[nei] = Node(nei.val)
q.append(nei)
old_to_new[old_curr].neighbors.append(old_to_new[nei])
return copy
return bfs(node) if node else None
class NeetSolution:
"""
DFS
"""
def cloneGraph(self, node: Optional['Node']) -> Optional['Node']:
oldToNew = {}
def dfs(node):
if node in oldToNew:
return oldToNew[node]
copy = Node(node.val)
oldToNew[node] = copy
for nei in node.neighbors:
copy.neighbors.append(dfs(nei))
return copy
return dfs(node) if node else None
class NeetSolution:
"""
BFS
"""
def cloneGraph(self, node: Optional['Node']) -> Optional['Node']:
if not node:
return None
oldToNew = {}
oldToNew[node] = Node(node.val)
q = deque([node])
while q:
cur = q.popleft()
for nei in cur.neighbors:
if nei not in oldToNew:
oldToNew[nei] = Node(nei.val)
q.append(nei)
oldToNew[cur].neighbors.append(oldToNew[nei])
return oldToNew[node]
Complexity
time: $O(n)$ where $n$ is number of nodes + edges.
space: $O(n)$