LC 1448 - Count Good Nodes in Binary Tree
LC 1448 - Count Good Nodes in Binary Tree
Question
Given a binary tree root, a node X in the tree is named good if in the path from root to X there are no nodes with a value greater than X.
Return the number of good nodes in the binary tree.
Example 1:
1
2
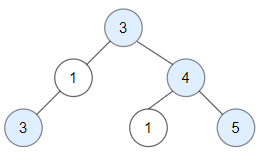
Input: root = [3,1,4,3,null,1,5]
Output: 4
Explanation: Nodes in blue are good. Root Node (3) is always a good node. Node 4 -> (3,4) is the maximum value in the path starting from the root. Node 5 -> (3,4,5) is the maximum value in the path Node 3 -> (3,1,3) is the maximum value in the path.
Example 2:
1
2
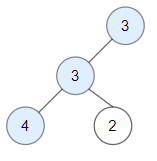
Input: root = [3,3,null,4,2]
Output: 3 **Explanation:** Node 2 -> (3, 3, 2) is not good, because "3" is higher than it.
Example 3:
1
2
Input: root = [1]
Output: 1
Explanation: Root is considered as good.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the binary tree is in the range
[1, 10^5]. - Each node’s value is between
[-10^4, 10^4].
Links
Question here and solution here
Solution
concept
Use a Preorder DFS to traverse the tree, we keep track:
- the max value so far in the path, this max value is evaluated at each node first (preorder)
- calculate the number of good nodes from left and right on the fly for each node, and return this value at each node
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def goodNodes(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
def dfs(curr, maxVal):
if not curr:
return 0
ans = 1 if curr.val >= maxVal else 0
maxVal = max(curr.val, maxVal)
ans += dfs(curr.left, maxVal)
ans += dfs(curr.right, maxVal)
return ans
return dfs(root, root.val)
class Solution:
def goodNodes(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
self.ans = 0
def dfs(cur, cur_max):
if not cur:
return
if cur.val >= cur_max:
self.ans += 1
cur_max = max(cur_max, cur.val)
dfs(cur.left, cur_max)
dfs(cur.right, cur_max)
return
dfs(root, float("-inf"))
return self.ans
Complexity
time: $O(n)$
space: $O(n)$
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.