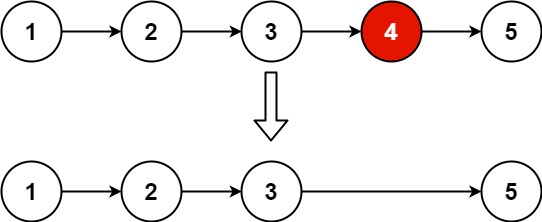
LC 19 - Remove Nth Node From End of List
Question
Given the head of a linked list, remove the nth node from the end of the list and return its head.
Example 1:
1
2
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
Output: [1,2,3,5]
Example 2:
1
2
Input: head = [1], n = 1
Output: []
Example 3:
1
2
Input: head = [1,2], n = 1
Output: [1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is
sz. 1 <= sz <= 300 <= Node.val <= 1001 <= n <= sz
Follow up: Could you do this in one pass?
Links
Question here and solution here
Solution
concept
We can store each node in a list and then either pop or skip the target node when reconnecting the linked list.
We can also use a two pointer to get the location of the node that supposed to be removed. We first choose r pointer to be n and l to be at the head. We notice that when r reach the end of the list, l will be at the index of the target node.
However, we need to be at the index before this node such that we can use the node.next = node.next.next to remove the target node, we do this by adding a dummy node in the front and start l at the dummy node while we put r at the nth position from head. (we need to traverse the linked list to put r there.) We then traverse both l and r until r reach the end. We can then use l.next = l.next.next to remove the target node.
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
"""
use a list to store all nodes
"""
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: Optional[ListNode], n: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
nodes = []
cur = head
while cur:
nodes.append(cur)
cur = cur.next
remove_idx = len(nodes) - n
nodes.pop(remove_idx) # remove the target node
if not nodes:
return None
# reconstruct the linked list
head = tail = nodes[0]
for i in range(1, len(nodes)):
tail.next = nodes[i]
tail = tail.next
tail.next = None
return head
class NeetSolution:
"""
use a list to store all nodes, but just by pass the nodes and reuse the linked list
"""
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: Optional[ListNode], n: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
nodes = []
cur = head
while cur:
nodes.append(cur)
cur = cur.next
removeIndex = len(nodes) - n
if removeIndex == 0:
return head.next
nodes[removeIndex - 1].next = nodes[removeIndex].next
return head
class Solution:
"""
two pointers
"""
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: Optional[ListNode], n: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
# create dummy
dummy = ListNode(0, head)
l = dummy
r = head
# move r to the idx where we can offset later
while n:
r = r.next
n -= 1
# move both l and r such that l can stop just before the idx of the target node
while r:
r = r.next
l = l.next
# skip/remove the target node
l.next = l.next.next
return dummy.next
Complexity
time: $O(n)$
space: $O(n)$ if store in list first, $O(1)$ if we use 2 pointers method.