LC 199 - Binary Tree Right Side View
LC 199 - Binary Tree Right Side View
Question
Given the root of a binary tree, imagine yourself standing on the right side of it, return the values of the nodes you can see ordered from top to bottom.
Example 1:
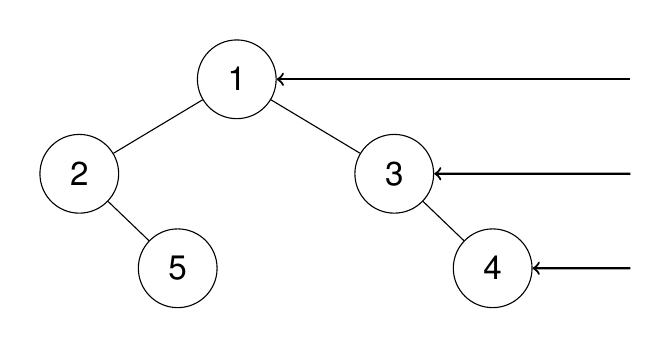
1
2
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
Output: [1,3,4]
Explanation:
Example 2:
1
2
Input: `root = [1,2,3,4,null,null,null,5]`
Output: `[1,3,4,5]`
Explanation:
Example 3:
1
2
Input: root = [1,null,3]
Output: [1,3]
Example 4:
1
2
Input: root = []
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Links
Question here and solution here
Solution
concept
Use a standard BFS but only keep the most right element for each level
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def rightSideView(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:
if not root:
return []
q = deque([root])
ans = []
while q:
tmp = []
for _ in range(len(q)):
node = q.popleft()
tmp.append(node.val)
if node.left:
q.append(node.left)
if node.right:
q.append(node.right)
ans.append(tmp[-1])
return ans
class NeetSolution:
"""
time complexity: O(n)
space complexity: O(n)
"""
def rightSideView(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:
res = []
q = deque([root])
while q:
rightSide = None # if root is None, return []
qLen = len(q)
for i in range(qLen):
node = q.popleft()
if node:
rightSide = node
q.append(node.left)
q.append(node.right)
# q is non-empty, but rightSide is could be None
if rightSide:
res.append(rightSide.val)
return res
Complexity
time: $O(n)$
space: $O(n)$
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.