LC 230 - Kth Smallest Element in a BST
Question
Given the root of a binary search tree, and an integer k, return the kth smallest value (1-indexed) of all the values of the nodes in the tree.
Example 1:
1
2
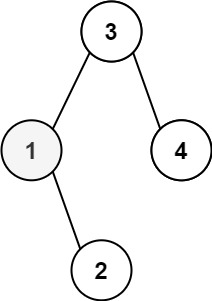
Input: root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1
Output: 1
Example 2:
1
2
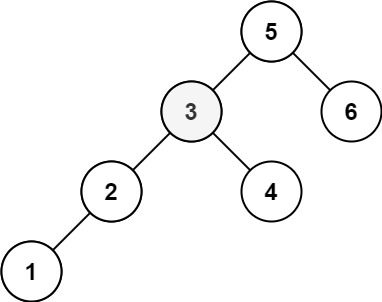
Input: `root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3`
Output: 3
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is
n. 1 <= k <= n <= 1040 <= Node.val <= 104
Follow up: If the BST is modified often (i.e., we can do insert and delete operations) and you need to find the kth smallest frequently, how would you optimize?
Links
Question here and solution here
Solution
concept
There are many ways to solve, we can traverse the tree and store all values in a heap and then find the k-th smallest element. We can also sort the values and then select the k-th smallest element accordingly.
Another way is to use in order traversal (left -> root -> right) and making use of the properties of BST, if we use in order traversal then the value we visit is already sorted.
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
"""
use heap
"""
def kthSmallest(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], k: int) -> int:
self.min_heap = []
def dfs(curr):
if not curr:
return
heapq.heappush(self.min_heap, curr.val)
dfs(curr.left)
dfs(curr.right)
return
dfs(root)
ans = float("inf")
while k:
ans = heapq.heappop(self.min_heap)
k -= 1
return ans
class Solution:
"""
in order traversal
"""
def kthSmallest(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], k: int) -> int:
arr = []
def dfs(node):
if not node:
return
dfs(node.left)
arr.append(node.val)
dfs(node.right)
dfs(root)
return arr[k - 1]
Complexity
time: $O(n)$
space: $O(n)$