LC 261 - Graph Valid Tree
LC 261 - Graph Valid Tree
Question
You have a graph of n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1. You are given an integer n and a list of edges where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an undirected edge between nodes ai and bi in the graph.
Return true if the edges of the given graph make up a valid tree, and false otherwise.
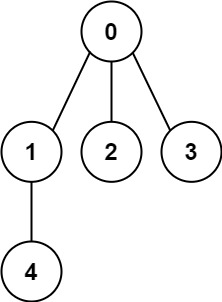
Example 1:
1
2
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[1,4]]
Output: true
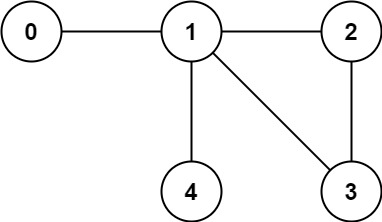
Example 2:
1
2
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[1,3],[1,4]]
Output: false
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 20000 <= edges.length <= 5000edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < nai != bi- There are no self-loops or repeated edges.
Links
Question here and solution here
Solution
concept
This question is very similar to 207. Course Schedule with one key differences: the graph is undirected This will cause two changes:
- in directed graph we are checking if the current (active) path has cycle exhaustively with DFS to follow through all possible path (with directions). we should use
visited.remove(curr_node)after we are done with the current node because if we don’t, it will give wrong answer. For example, our active path isA -> B -> C -> E -> Fand there is not cycle, and if we do not remove the nodes during backtracking (i.e.C, E, F) and go fromA -> B -> D -> E -> Fwe will falsely conclude there is a cycle sinceEandFis in the visited set. But in a directed graph, there is no cycle. If the graph is undirected, then this is a cycle and we do not removing nodes during traversal (if we remove, it will be wrong since this is a cycle if the graph is undirected). So in undirected graph where we check for cycles, we do not remove node. - the adjacency list has to add both way (i.e. treat the graph as pointing both directions). This means that during DFS, the node’s parents will be visited since it is also the neighbors, this will cause the algorithm to falsely identify cycle. So we have to ignore the parent node during DFS.
graph TD A --> B B --> C B --> D D --> E C --> E E --> F
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
class Solution:
def validTree(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
adj_list = {i: [] for i in range(n)}
for u, v in edges:
adj_list[u].append(v)
adj_list[v].append(u)
visited = set()
def dfs(node, parent):
if node in visited:
return False # cycle detected
visited.add(node)
for nei in adj_list[node]:
if nei == parent: # ignore back edge to parent
continue
if not dfs(nei, node):
return False
return True
if dfs(0, -1) and len(visited) == n:
return True
else:
return False
Complexity
time: $O(V + E)$
space: $O(V + E)$
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.