LC 4 - Median of Two Sorted Arrays
Question
Given two sorted arrays nums1 and nums2 of size m and n respectively, return the median of the two sorted arrays.
The overall run time complexity should be O(log (m+n)).
Example 1:
1
2
Input: nums1 = [1,3], nums2 = [2]
Output: 2.00000
Explanation: merged array = [1,2,3] and median is 2.
Example 2:
1
2
Input: nums1 = [1,2], nums2 = [3,4]
Output: 2.50000
Explanation: merged array = [1,2,3,4] and median is (2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5.
Constraints:
nums1.length == mnums2.length == n0 <= m <= 10000 <= n <= 10001 <= m + n <= 2000-106 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 106
Links
Question here and solution here
Solution
concept
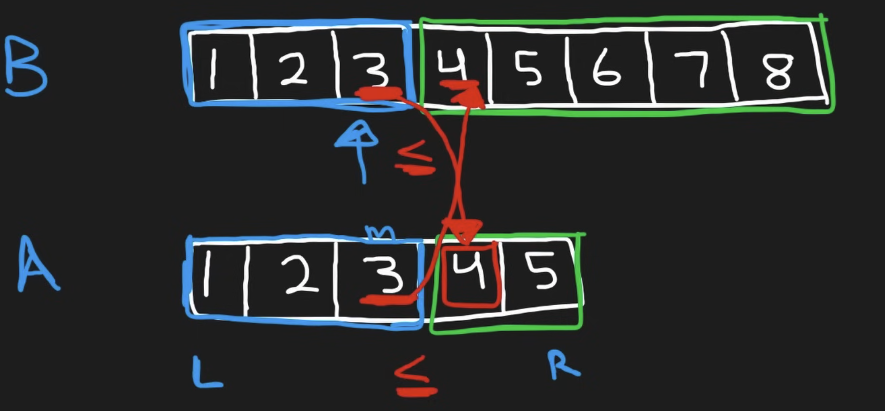
The main idea is to run binary search on the shorter list to deduce the required index of the cut off point in the longer list. The two list A and B (A is the shorter one) are given and we start with A where we assume the left part of the list belongs to the left part of the combined list. In the picture below there are total 13 numbers so there should be 6 numbers in the left portion (if we want to calculate the median, we need to figure out the middle point in the combined sorted array), so this leave us 6-3=3 numbers to be found in array B. We then check the boundary Aleft (in A, blue 3), Aright (in A, green 4), Bleft (in B, blue 3), Bright (in B, green 4) which are the 4 index in the A/B arrays to see if the condition is satisfied: Aleft < Bright and Bleft < Aright, if this is satisfied then we found the boundary of the middle point in the combined list. if not we need to do binary search to move the m , 0 -> m is the subarray that will be in the final left portion and the in each search the subarray B will be adjusted accordingly and the boundary conditions (Aleft < Bright and Bleft < Aright) will be checked.
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
class NeetSolution:
"""
time complexity: O(log(m+n))
run binary search on the shorter list
deduce the required index of the cut off point in the longer list
check if the cut off point is valid by comparing the left and right partition of the two lists
"""
def findMedianSortedArrays(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> float:
total = len(nums1) + len(nums2)
half = total//2
if len(nums1) <= len(nums2):
A = nums1
B = nums2
else:
A = nums2
B = nums1
# for binary search in A only
l, r = 0, len(A) - 1
while True:
# index of midpt in A
i = (l + r) // 2
# index of the cut off point in B
j = half - (i + 1) - 1
# edge case of out-of-bound index
# esp the while loop is set to True instead of the usual L <= R for binary search
# if A is an empty list, or we have search too left on A
Aleft = A[i] if i >= 0 else float("-infinity")
# if we want to include all elements in A in the final left partition -> searched too right
Aright = A[i + 1] if (i + 1) < len(A) else float("infinity")
# same as A
Bleft = B[j] if j >= 0 else float("-infinity")
# same as A
Bright = B[j + 1] if (j + 1) < len(B) else float("infinity")
# the partition is valid
if Aleft <= Bright and Bleft <= Aright:
# odd
if total % 2:
return min(Aright, Bright)
# even
else:
return (max(Aleft, Bleft) + min(Aright, Bright)) / 2
# need to reduce the partition in A
elif Aleft > Bright:
r = i - 1
# need to increase the partition in A such that the partition in B is reduced
else:
l = i + 1
Complexity
time: $O(n)$
space: $O(n)$