LC 417 - Pacific Atlantic Water Flow
Question
There is an m x n rectangular island that borders both the Pacific Ocean and Atlantic Ocean. The Pacific Ocean touches the island’s left and top edges, and the Atlantic Ocean touches the island’s right and bottom edges.
The island is partitioned into a grid of square cells. You are given an m x n integer matrix heights where heights[r][c] represents the height above sea level of the cell at coordinate (r, c).
The island receives a lot of rain, and the rain water can flow to neighboring cells directly north, south, east, and west if the neighboring cell’s height is less than or equal to the current cell’s height. Water can flow from any cell adjacent to an ocean into the ocean.
Return a 2D list of grid coordinates result where result[i] = [ri, ci] denotes that rain water can flow from cell (ri, ci) to both the Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
Example 1:
1
2
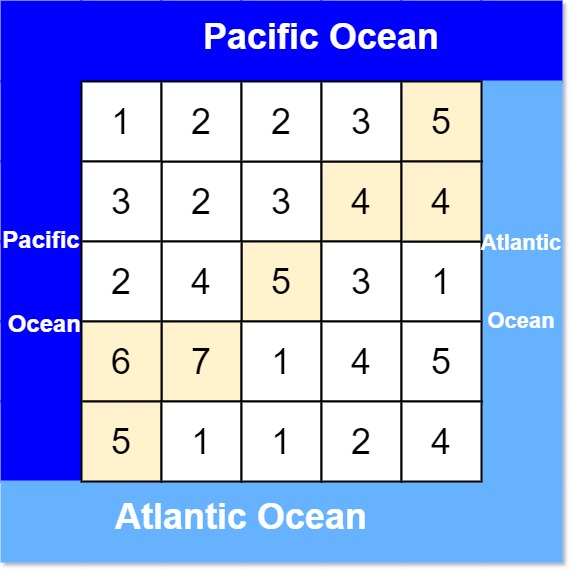
Input: heights = [[1,2,2,3,5],[3,2,3,4,4],[2,4,5,3,1],[6,7,1,4,5],[5,1,1,2,4]]
Output: [[0,4],[1,3],[1,4],[2,2],[3,0],[3,1],[4,0]] **Explanation:** The following cells can flow to the Pacific and Atlantic oceans, as shown below:
Example 2:
1
2
Input: heights = [[1]]
Output: [[0,0]] **Explanation:** The water can flow from the only cell to the Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
Constraints:
m == heights.lengthn == heights[r].length1 <= m, n <= 2000 <= heights[r][c] <= 105
Links
Question here and solution here
Solution
concept
The brute force way is to do DFS from each cell and see if it can reach the other side. The time complexity will be $O(mn4^{m*n})$ The more optimised way is to run DFS from the edges and see what cells it can reach from 4 borders. We will have 2 visited set to keep track what cells can be reached from atlantic and pacific.We then check if any cells exist in both set and that is the answer.
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
class Solution:
"""
brute force DFS
"""
def pacificAtlantic(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
ROWS, COLS = len(heights), len(heights[0])
directions = [[0,1],[1,0], [0,-1], [-1,0]]
ans = []
def dfs(r, c, prev_val):
nonlocal pacific, atlantic
if r < 0 or c < 0:
pacific = True
return
if r >= ROWS or c >= COLS:
atlantic = True
return
if (r,c) in visited or heights[r][c] > prev_val:
return
visited.add((r,c))
for dr, dc in directions:
dfs(r+dr, c+dc, heights[r][c])
if pacific and atlantic:
break
for r in range(ROWS):
for c in range(COLS):
visited = set()
pacific = False
atlantic = False
dfs(r,c,heights[r][c])
if pacific and atlantic:
ans.append([r,c])
return ans
class Solution:
"""
DFS
"""
def pacificAtlantic(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
ROWS, COLS = len(heights), len(heights[0])
directions = [[0,1],[1,0], [0,-1], [-1,0]]
pacific, atlantic = set(), set()
ans = []
def dfs(r, c, visited, prev_val):
if (r < 0 or r >= ROWS or
c < 0 or c >= COLS or
(r,c) in visited or
heights[r][c] < prev_val):
return
visited.add((r,c))
for dr, dc in directions:
dfs(r + dr, c + dc, visited, heights[r][c])
for r in range(ROWS):
dfs(r, 0, pacific, heights[r][0]) # we choose the starting val as the val itself, since it has no previous value but this placeholder starting value allows the algo to flow.
dfs(r, COLS - 1, atlantic, heights[r][COLS - 1])
for c in range(COLS):
dfs(0, c, pacific, heights[0][c])
dfs(ROWS - 1, c, atlantic, heights[ROWS -1][c])
for r in range(ROWS):
for c in range(COLS):
if (r,c) in atlantic and (r,c) in pacific:
ans.append([r,c])
return ans
Complexity
time: $O(mn)$
space: $O(mn)$