LC 45 - Jump Game II
Question
You are given a 0-indexed array of integers nums of length n. You are initially positioned at index 0.
Each element nums[i] represents the maximum length of a forward jump from index i. In other words, if you are at index i, you can jump to any index (i + j) where:
0 <= j <= nums[i]andi + j < n
Return the minimum number of jumps to reach index n - 1. The test cases are generated such that you can reach index n - 1.
Example 1:
1
2
Input: nums = [2,3,1,1,4]
Output: 2
Explanation: The minimum number of jumps to reach the last index is 2. Jump 1 step from index 0 to 1, then 3 steps to the last index.
Example 2:
1
2
Input: nums = [2,3,0,1,4]
Output: 2
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1040 <= nums[i] <= 1000- It’s guaranteed that you can reach
nums[n - 1].
Links
Question here and solution here
Solution
concept
The greedy solution is like a 1-D BFS, where we keep a window (l,r) and we check each window how far the elements within each level can jump the furthest. This will be the right pointer, and the left pointer will be updated as old right pointer + 1 The number of level (or step) is the answer. 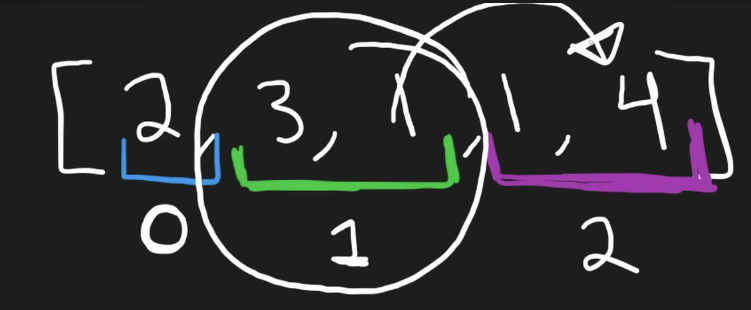
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
class Solution:
"""
brute force DFS
"""
def jump(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
def dfs(i):
ans = float("inf")
if i == len(nums) - 1:
return 0
if nums[i] == 0:
return float("inf")
end = min(len(nums) - 1, i + nums[i])
for j in range(i + 1, end + 1):
ans = min(ans, 1 + dfs(j))
return ans
res = dfs(0)
return res
class Solution:
"""
dp: top down (memoization)
"""
def jump(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
cache = {}
def dfs(i):
ans = float("inf")
if i == len(nums) - 1:
return 0
if nums[i] == 0:
return float("inf")
if i in cache:
return cache[i]
end = min(len(nums) - 1, i + nums[i])
for j in range(i + 1, end + 1):
ans = min(ans, 1 + dfs(j))
cache[i] = ans
return cache[i]
res = dfs(0)
return res
class Solution:
"""
dp: bottom up
"""
def jump(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
dp = [float("inf")] * len(nums)
dp[-1] = 0
for i in range(len(nums)-2, -1, -1):
end = min(len(nums)-1, nums[i] + i)
for j in range(i + 1, end + 1):
dp[i] = min(dp[i], dp[j] + 1)
return dp[0]
class Solution:
"""
greedy
"""
def jump(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
step = 0
l = r = 0
while r < len(nums) - 1:
furthest = 0
for i in range(l, r + 1):
furthest = max(furthest, i + nums[i])
step += 1
l = r + 1
r = furthest
return step
Complexity
time: $O(n^2)$ if DP, $O(n)$ if greedy
space: $O(n)$