LC 494 - Target Sum
Question
You are given an integer array nums and an integer target.
You want to build an expression out of nums by adding one of the symbols '+' and '-' before each integer in nums and then concatenate all the integers.
- For example, if
nums = [2, 1], you can add a'+'before2and a'-'before1and concatenate them to build the expression"+2-1".
Return the number of different expressions that you can build, which evaluates to target.
Example 1:
1
2
Input: nums = [1,1,1,1,1], target = 3
Output: 5
Explanation: There are 5 ways to assign symbols to make the sum of nums be target 3. -1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 3 +1 - 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 3 +1 + 1 - 1 + 1 + 1 = 3 +1 + 1 + 1 - 1 + 1 = 3 +1 + 1 + 1 + 1 - 1 = 3
Example 2:
1
2
Input: nums = [1], target = 1
Output: 1
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 200 <= nums[i] <= 10000 <= sum(nums[i]) <= 1000-1000 <= target <= 1000
Links
Question here and solution here
Solution
concept
The bottom up solution requires a 2D grid where the y-axis is the the index i same as the DFS solution. and the x-axis is the cur_sum that is possible to sum with the current number at ith index It is defined that the first row at 0 will be 0, this means one way to sum to 0 with the first 0 elements, the number in the grid itself represent the number of ways it can be used to sum. We do not need to populate the whole grid (hence in this question the dp is a defaultdict) We are only interested in the purple box number which is the answer (i.e. after we go through all 5 numbers, the target sum is 3, and what is the total number of ways ?) 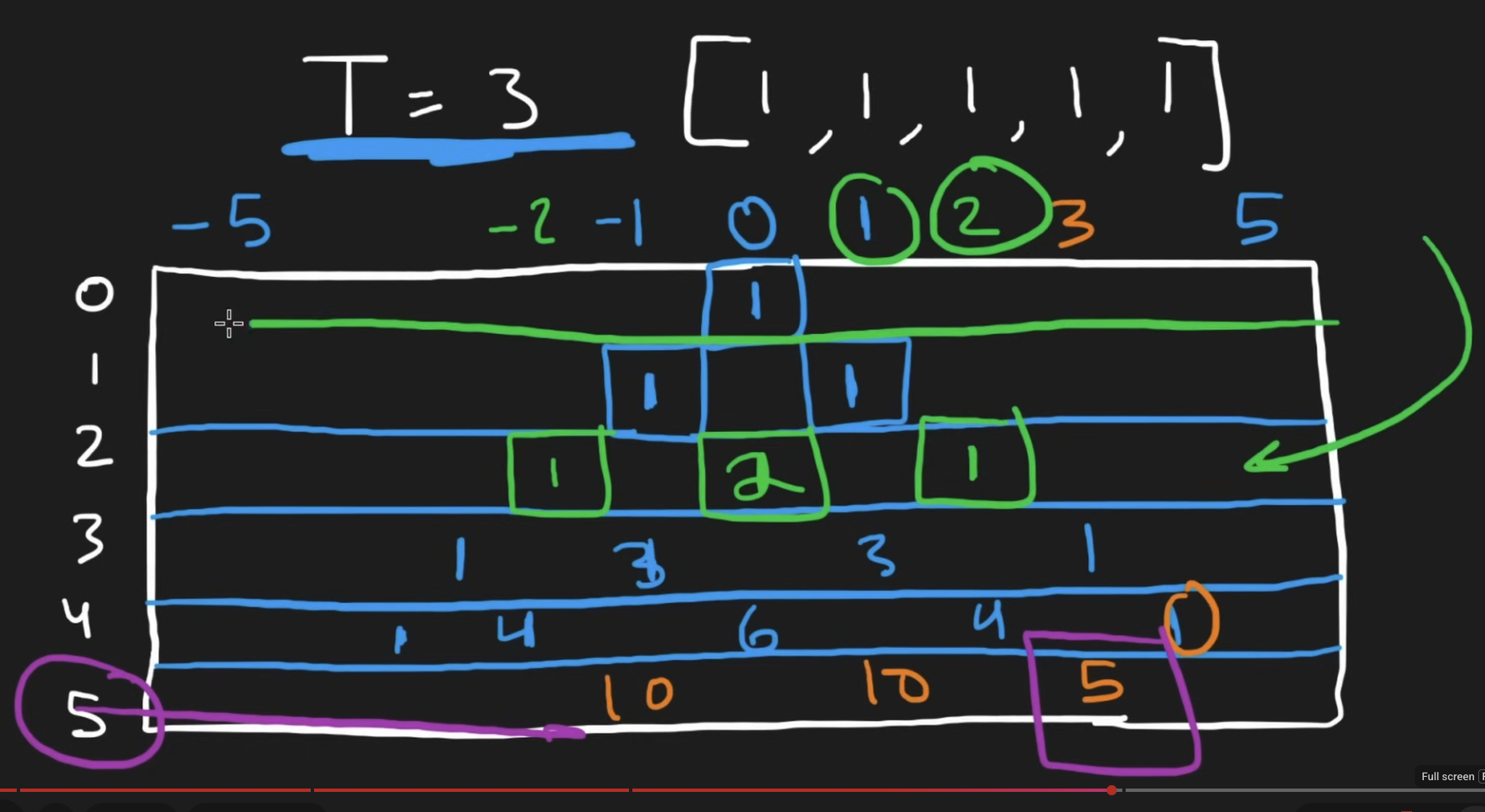
For the space optimized solution, notice that we only need the previous row to compute the next row.
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
class Solution:
"""
brute force dfs
TLE
"""
def findTargetSumWays(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
def dfs(i, cur_sum):
if i >= len(nums):
if cur_sum == target:
return 1
else:
return 0
plus_option = dfs(i + 1, cur_sum + nums[i])
minus_option = dfs(i + 1, cur_sum - nums[i])
return plus_option + minus_option
return dfs(0, 0)
class Solution:
"""
top down: memoization
"""
def findTargetSumWays(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
cache = {}
def dfs(i, cur_sum):
if (i, cur_sum) in cache:
return cache[(i, cur_sum)]
if i >= len(nums):
if cur_sum == target:
return 1
else:
return 0
plus_option = dfs(i + 1, cur_sum + nums[i])
minus_option = dfs(i + 1, cur_sum - nums[i])
cache[(i, cur_sum)] = plus_option + minus_option
return cache[(i, cur_sum)]
return dfs(0, 0)
class Solution:
"""
bottom up solution
"""
def findTargetSumWays(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
dp = [defaultdict(int) for i in range(len(nums) + 1)]
dp[0][0] = 1 # one way to sum to 0 with first 0 element
for i in range(len(nums)):
for cur_sum, count in dp[i].items():
dp[i + 1][cur_sum + nums[i]] += count
dp[i + 1][cur_sum - nums[i]] += count
return dp[len(nums)][target]
class Solution:
"""
bottom up solution
space optimized
"""
def findTargetSumWays(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
dp = defaultdict(int)
dp[0] = 1 # one way to sum to 0
for i in range(len(nums)):
next_dp = defaultdict(int)
for cur_sum, count in dp.items():
next_dp[cur_sum + nums[i]] += count
next_dp[cur_sum - nums[i]] += count
dp = next_dp
return dp[target]
Complexity
time: $O(nm)$
space: $O(nm)$ or $O(m)$
where n is the length of the array nums and m is the sum of all the elements in the array