LC 518 - Coin Change II
Question
You are given an integer array coins representing coins of different denominations and an integer amount representing a total amount of money.
Return the number of combinations that make up that amount. If that amount of money cannot be made up by any combination of the coins, return 0.
You may assume that you have an infinite number of each kind of coin.
The answer is guaranteed to fit into a signed 32-bit integer.
Example 1:
1
2
Input: amount = 5, coins = [1,2,5]
Output: 4
Explanation: there are four ways to make up the amount: 5=5 5=2+2+1 5=2+1+1+1 5=1+1+1+1+1
Example 2:
1
2
Input: amount = 3, coins = [2]
Output: 0
Explanation: the amount of 3 cannot be made up just with coins of 2.
Example 3:
1
2
Input: amount = 10, coins = [10]
Output: 1
Constraints:
1 <= coins.length <= 3001 <= coins[i] <= 5000- All the values of
coinsare unique. 0 <= amount <= 5000
Links
Question here and solution here
Solution
concept
The question is quite similar to [[322. Coin Change]]. One thing to note that if we use cur_sum, it will work on memoization (although still TLE). This is because we are not looking for that specific minimum combination of coins but we are storing the number of combinations at specific index and current sum. Also note that the for loop used in [[322. Coin Change]] means we are looking at permutation and not combination since we need to go through every coins in each iterations. (i.e. we are looking at 1+2+2 and 2+1+2 etc), so if we reuse the code for this question we will be over-counting.
For the 2D DP bottom up solution, the main idea is to draw the 2D grid: the x-axis is the amount we are targeting (in the actual code it is from 0 -> 5) while the y-axis is the coins that we have. At each grid, it will store the number of combinations to reach that particular amount with coins that from the row and below, i.e. in the picture below, it is 1 combinations to sum to amount = 0 with coin 2 and 5. (1 combination sum to 0 is for mathematical correctness sake) 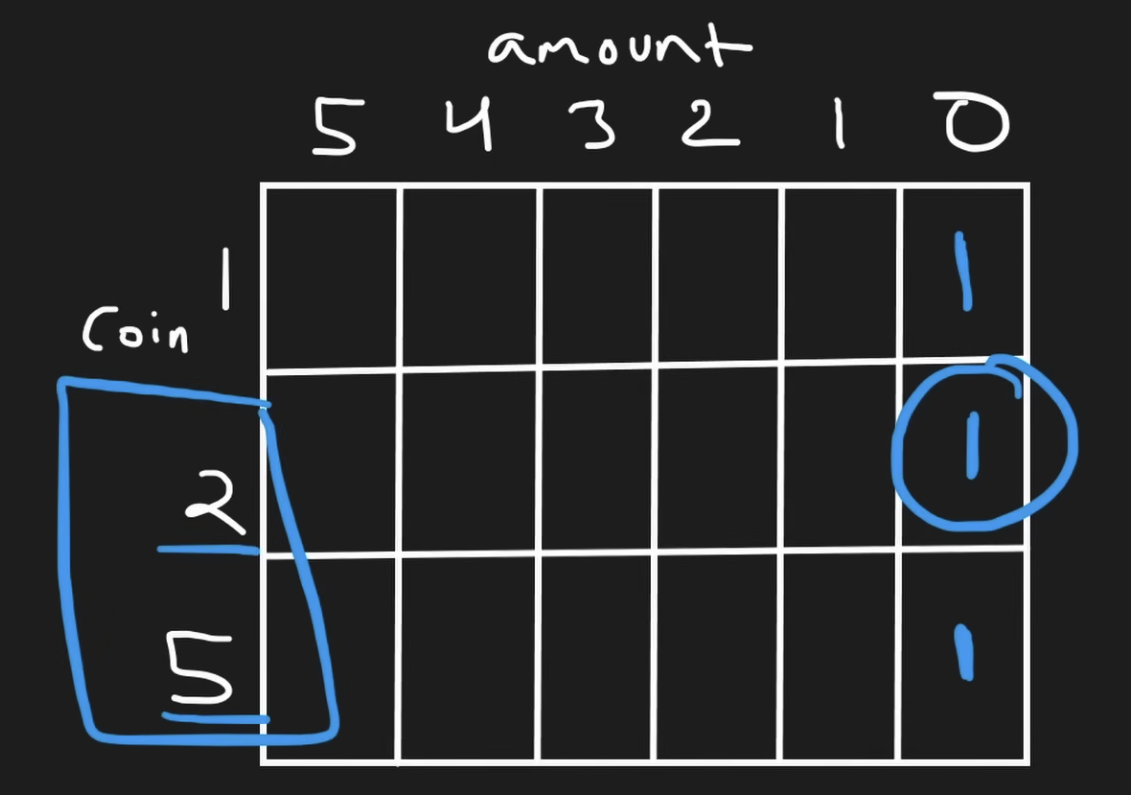
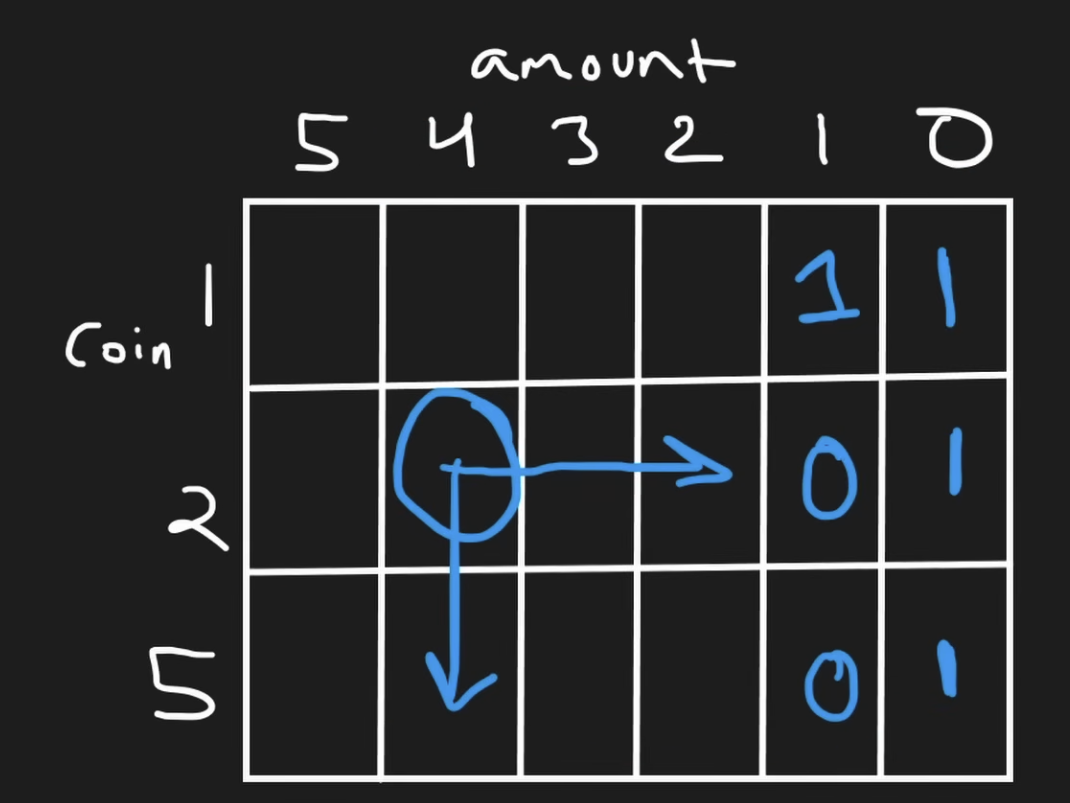
At any one time, if we want to calculate the grid, we will need to take a look at 2 directions and sum them:
- if we use the coin, e.g. the amount is
4and the coin is2, the remain amount will be4-2=2and we will have to look to the right to get the cells. Since we have already calculated the total combinations withamount = 2, we will use it - if we skip the coin, then we will have to look exactly one row down, since the row below is the the amount = 4 with all the coins. (here is just coin 5, but it can be more coin type, the key thing here is that this cell contains all combinations from coin 5 and below.)
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
class Solution:
"""
brute force backtracking
keep track of current sum
TLE
"""
def change(self, amount: int, coins: List[int]) -> int:
ans = 0
def dfs(i, cur_sum):
nonlocal ans
if i >= len(coins) or cur_sum > amount:
return
if cur_sum == amount:
ans += 1
return
dfs(i, cur_sum + coins[i])
dfs(i + 1, cur_sum)
dfs(0,0)
return ans
class Solution:
"""
NeetCode version of memoization
keep track of current sum
this works
"""
def change(self, amount: int, coins: List[int]) -> int:
ans = 0
cache = {}
def dfs(i, cur_sum):
nonlocal ans
if i >= len(coins) or cur_sum > amount:
return
if cur_sum == amount:
ans += 1
cache[(i, cur_sum)] = ans
return
if (i, cur_sum) in cache:
return cache[(i, cur_sum)]
dfs(i, cur_sum + coins[i])
dfs(i + 1, cur_sum)
dfs(0,0)
return ans
class Solution:
def change(self, amount: int, coins: List[int]) -> int:
cache = {}
def dfs(i, cur_sum):
if cur_sum == amount:
return 1
if cur_sum > amount or i >= len(coins):
return 0
if (i, cur_sum) in cache:
return cache[(i, cur_sum)]
use = dfs(i, cur_sum + coins[i])
skip = dfs(i + 1, cur_sum)
cache[(i, cur_sum)] = use + skip
return cache[(i, cur_sum)]
return dfs(0, 0)
class Solution:
"""
brute force
use remain amount
TLE
"""
def change(self, amount: int, coins: List[int]) -> int:
def dfs(i, remain):
if remain == 0:
return 1
if remain < 0 or i >= len(coins):
return 0
use = dfs(i, remain - coins[i])
skip = dfs(i + 1, remain)
return use + skip
return dfs(0, amount)
class Solution:
"""
top down: memoization
use remain amount
"""
def change(self, amount: int, coins: List[int]) -> int:
cache = {}
def dfs(i, remain):
if (i, remain) in cache:
return cache[(i, remain)]
if remain == 0:
return 1
if remain < 0 or i >= len(coins):
return 0
use = dfs(i, remain - coins[i])
skip = dfs(i + 1, remain)
cache[(i, remain)] = use + skip
return cache[(i, remain)]
return dfs(0, amount)
class Solution:
"""
2D DP bottom up
need sort the coin first
"""
def change(self, amount: int, coins: List[int]) -> int:
coins.sort()
dp = [[0] * (amount + 1) for _ in range(len(coins) + 1)]
for i in range(len(coins) + 1):
dp[i][0] = 1
for i in range(len(coins) - 1, -1, -1):
for cur_amt in range(amount + 1):
if cur_amt >= coins[i]:
# only update skip if condion is true, this requires sorting the coins first
dp[i][cur_amt] = dp[i + 1][cur_amt]
dp[i][cur_amt] += dp[i][cur_amt - coins[i]]
return dp[0][amount]
class Solution:
"""
2D DP bottom up
no need to sort coins first
"""
def change(self, amount: int, coins: List[int]) -> int:
dp = [[0] * (amount + 1) for _ in range(len(coins) + 1)]
for i in range(len(coins) + 1):
dp[i][0] = 1
for i in range(len(coins) - 1, -1, -1):
coin = coins[i]
for cur_amt in range(amount + 1):
# always can skip coin i
dp[i][cur_amt] = dp[i + 1][cur_amt]
# if we can use coin i, add ways using it
if cur_amt >= coin:
dp[i][cur_amt] += dp[i][cur_amt - coin]
return dp[0][amount]
class Solution:
"""
2D DP bottom up
space optmised
only store 2 rows at any one time
"""
def change(self, amount: int, coins: List[int]) -> int:
dp = [0] * (amount + 1)
dp[0] = 1
for i in range(len(coins) - 1, -1, -1):
nextDP = [0] * (amount + 1)
nextDP[0] = 1
for cur_amt in range(1, amount + 1):
nextDP[cur_amt] = dp[cur_amt]
if cur_amt - coins[i] >= 0:
nextDP[cur_amt] += nextDP[cur_amt - coins[i]]
dp = nextDP
return dp[amount]
Complexity
time: $O(na)$
space: $O(na)$ or $O(n)$