LC 62 - Unique Paths
Question
There is a robot on an m x n grid. The robot is initially located at the top-left corner (i.e., grid[0][0]). The robot tries to move to the bottom-right corner (i.e., grid[m - 1][n - 1]). The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time.
Given the two integers m and n, return the number of possible unique paths that the robot can take to reach the bottom-right corner.
The test cases are generated so that the answer will be less than or equal to 2 * 109.
Example 1:
1
2
Input: m = 3, n = 7
Output: 28
Example 2:
1
2
Input: m = 3, n = 2
Output: 3
Explanation: From the top-left corner, there are a total of 3 ways to reach the bottom-right corner:
- Right -> Down -> Down
- Down -> Down -> Right
- Down -> Right -> Down
Constraints:
1 <= m, n <= 100
Links
Question here and solution here
Solution
concept
In the bottom-up solution, at each cell we compute the number of unique path to the goal. Note that this is the basically the sum of the number of paths from the right cell and bottom cell. (i.e. dp[r][c] = dp[r+1][c] + dp[r][c+1])
Note that for this question the bottom row and right col is always going to be filled with 1. For ease of calculation, we can add an extra row and col of zero. 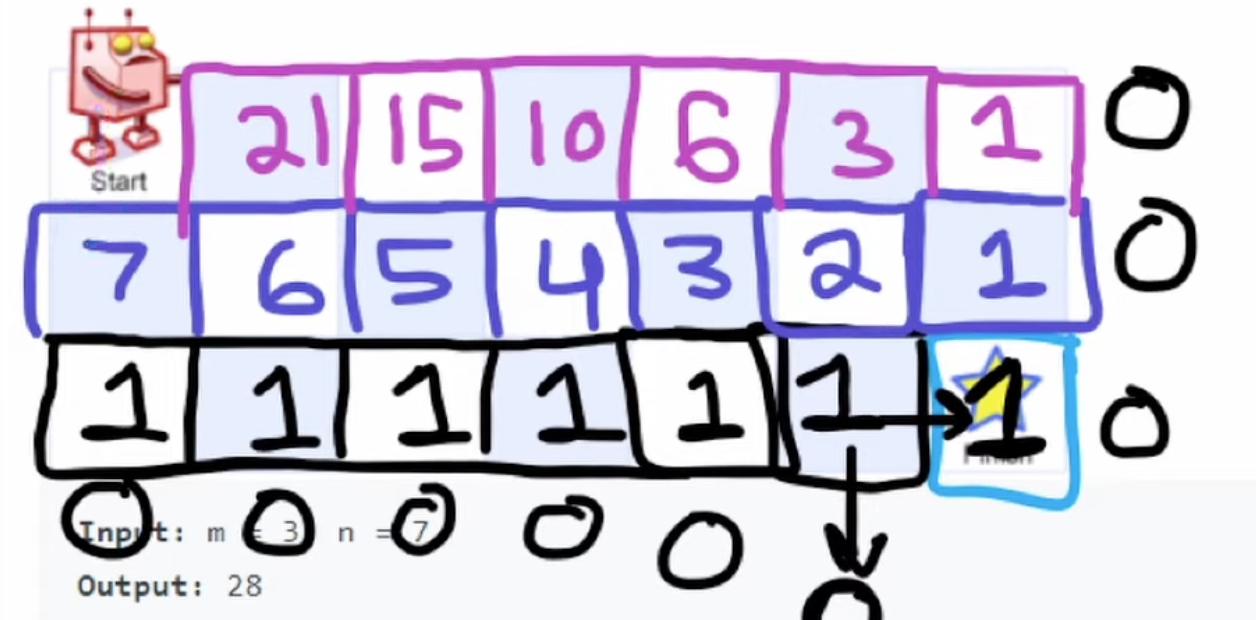
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
class Solution:
"""
brute force backtrackking
TLE
"""
def uniquePaths(self, m: int, n: int) -> int:
ROWS, COLS = m, n
path = set()
ans = 0
directions = [[0,1], [1,0]]
def dfs(r, c):
nonlocal ans
if r == ROWS - 1 and c == COLS - 1:
ans += 1
return
if (r < 0 or r >= ROWS
or c < 0 or c >= COLS
or (r, c) in path):
return
path.add((r,c))
for dr, dc in directions:
dfs(r + dr, c + dc)
path.remove((r,c))
dfs(0,0)
return ans
class Solution:
"""
top-down solution: memoization
"""
def uniquePaths(self, m: int, n: int) -> int:
ROWS, COLS = m, n
path = set()
directions = [[0,1], [1,0]]
cache = [[0] * COLS for i in range(ROWS)]
def dfs(r, c):
nonlocal ans
if r == ROWS - 1 and c == COLS - 1:
ans += 1
return
if (r < 0 or r >= ROWS
or c < 0 or c >= COLS
or (r, c) in path):
return
# already check (r,c) is bounded
if cache[r][c] != 0:
ans += cache[r][c]
return
path.add((r,c))
for dr, dc in directions:
dfs(r + dr, c + dc)
path.remove((r,c))
for r in range(ROWS - 1, -1, -1):
for c in range(COLS - 1, -1, -1):
ans = 0
dfs(r,c)
cache[r][c] = ans
return cache[0][0]
class Solution:
"""
bottom up solution
"""
def uniquePaths(self, m: int, n: int) -> int:
ROWS, COLS = m, n
# extra row and col of 0 for ease of calculation
dp = [[0]*(COLS + 1) for i in range(ROWS + 1)]
# base case of the goal is 1
dp[ROWS - 1][COLS - 1] = 1
for r in range(ROWS - 1, -1, -1):
for c in range(COLS - 1, -1, -1):
# use += for the base case calculation, else it will be overwritten by 0
dp[r][c] += dp[r + 1][c] + dp[r][c + 1]
return dp[0][0]
class Solution:
"""
bottom-up solution
space-optimised
"""
def uniquePaths(self, m: int, n: int) -> int:
row = [1] * n # current row
for i in range(m - 1):
abv_row = [1] * n
for j in range(n - 2, -1, -1):
abv_row[j] = abv_row[j + 1] + row[j]
row = abv_row
return row[0]
Complexity
time: $O(mn)$
space: $O(n)$