LC 72 - Edit Distance
Question
Given two strings word1 and word2, return the minimum number of operations required to convert word1 to word2.
You have the following three operations permitted on a word:
- Insert a character
- Delete a character
- Replace a character
Example 1:
1
2
Input: word1 = "horse", word2 = "ros"
Output: 3
Explanation: horse -> rorse (replace ‘h’ with ‘r’) rorse -> rose (remove ‘r’) rose -> ros (remove ‘e’)
Example 2:
1
2
Input: word1 = "intention", word2 = "execution"
Output: 5
Explanation: intention -> inention (remove ‘t’) inention -> enention (replace ‘i’ with ‘e’) enention -> exention (replace ‘n’ with ‘x’) exention -> exection (replace ‘n’ with ‘c’) exection -> execution (insert ‘u’)
Constraints:
0 <= word1.length, word2.length <= 500word1andword2consist of lowercase English letters.
Links
Question here and solution here
Solution
concept
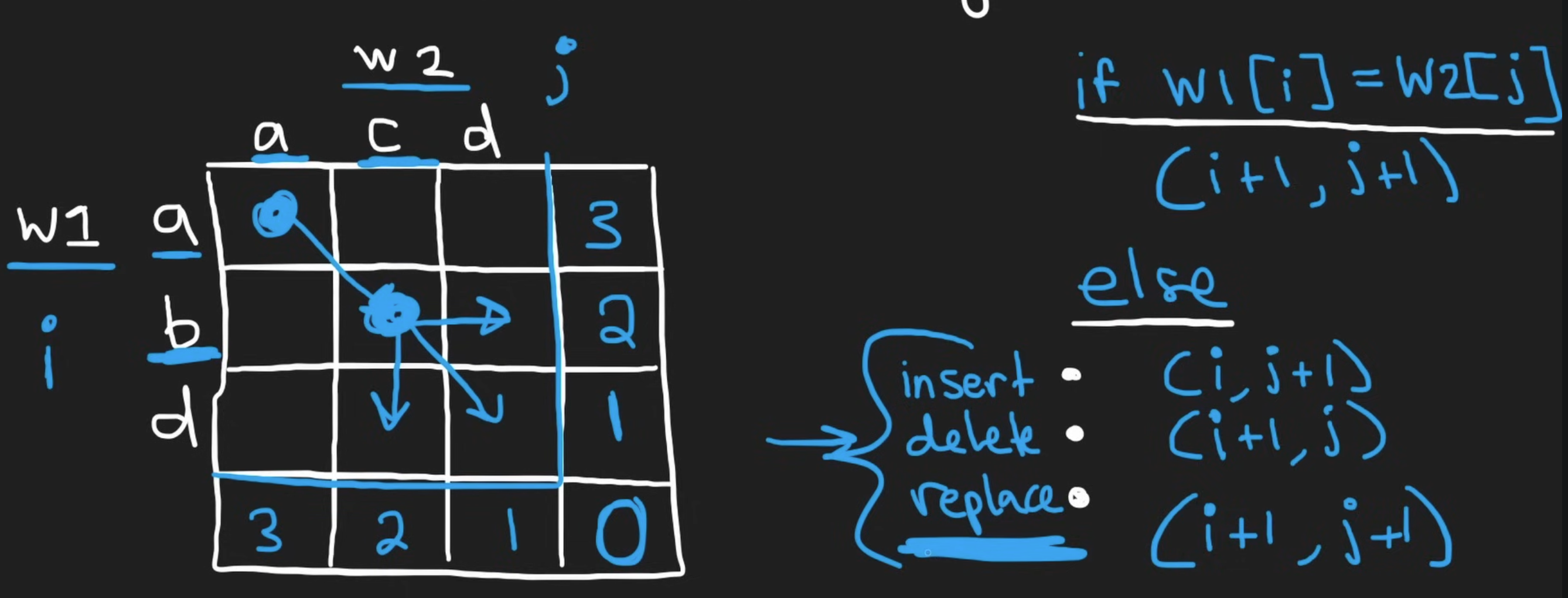
If we have two words word1 and word2, and i and j are the index respectively, we will have a few scenario if we want to make word1 -> word2:
- if
word1[i] == word2[j], then there is no operation needed.- we need to shift both pointers since they are matched:
(i,j)->(i+1,j+1)
- we need to shift both pointers since they are matched:
- if
word1[i] != word2[j], then there will be one operation needed to operate onword1, we will go down all three path, but each with different pointer movement:- insert: our
ipointer stays the same since we just insert a char at indexi, but since after insertingword2atjis satisfied, we have to move thejpointer:(i, j) -> (i, j+1)
- delete: this is the same as skipping the current char in
word1, but since there is no match inword2yet, so thejpointer remains the same:(i, j)->(i+1, j)
- replace: this means that we are able to match after replacing, so both pointers advanced. The difference between this and the already-matched in the first case is that this one needs one operation and the already-matched does not need an operation
(i, j)->(i+1, j+1)
- insert: our
The base case will be either word run out:
- if
word1run out first, this means thatihas reached the end, then the number of operations needed is inserting the remaining of theword2intoword1, this means the operations needed islen(word2) - j - if
word2run out first, this means thatjhas reached the end, then the number of operations needed is deleting the remaining of theword1such that it is equal toword2, this means the operations needed islen(word1) - i
For the bottom up solution, the concept is very similar:
- at each cell, we record the minimum number of operations needed for the sub problems for
word1[i:]andword2[j:] - we have our base cases at the right and bottom and it is basically the cases where either string runs out. This is the same base cases as the above
- if
word1[i] == word2[j]then we just take the diagonal bottom right - else we will take look at the 3 squares and find the minimum of these and add one operation on top of it.
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
class Solution:
"""
brute force DFS
TLE
"""
def minDistance(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:
def dfs(i,j):
if i == len(word1):
return len(word2) - j
if j == len(word2):
return len(word1) - i
# already matched
if word1[i] == word2[j]:
return dfs(i + 1, j + 1) # no operation needed
# choose the min among the three operations
ops = min(dfs(i + 1, j), dfs(i, j + 1), dfs(i + 1, j + 1))
return 1 + ops # one operation needed
return dfs(0,0)
class Solution:
def minDistance(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:
"""
top down: memoization
"""
cache = {}
def dfs(i,j):
if i == len(word1):
return len(word2) - j
if j == len(word2):
return len(word1) - i
if (i,j) in cache:
return cache[(i, j)]
if word1[i] == word2[j]:
cache[(i,j)] = dfs(i + 1, j + 1)
return cache[(i,j)]
ops = min(dfs(i + 1, j), dfs(i, j + 1), dfs(i + 1, j + 1))
cache[(i,j)] = 1 + ops
return cache[(i,j)]
return dfs(0,0)
class Solution:
"""
bottom up solution
"""
def minDistance(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:
dp = [[float("inf")] * (len(word2) + 1) for _ in range(len(word1) + 1)]
for i in range(len(word1) + 1):
dp[i][len(word2)] = len(word1) - i
for j in range(len(word2) + 1):
dp[len(word1)][j] = len(word2) - j
for i in range(len(word1)-1, -1, -1):
for j in range(len(word2)-1, -1, -1):
if word1[i] == word2[j]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j + 1]
else:
dp[i][j] = 1 + min(dp[i + 1][j + 1], dp[i][j + 1], dp[i + 1][j])
return dp[0][0]
class NeetSolution:
"""
bottom up solution
space optimized
"""
def minDistance(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:
m, n = len(word1), len(word2)
if m < n:
m, n = n, m
word1, word2 = word2, word1
dp = [0] * (n + 1)
nextDp = [0] * (n + 1)
for j in range(n + 1):
dp[j] = n - j
for i in range(m - 1, -1, -1):
nextDp[n] = m - i
for j in range(n - 1, -1, -1):
if word1[i] == word2[j]:
nextDp[j] = dp[j + 1]
else:
nextDp[j] = 1 + min(dp[j], nextDp[j + 1], dp[j + 1])
dp = nextDp[:]
return dp[0]
Complexity
time: $O(mn)$
space: $O(mn)$ or $O(min(m,n))$