LC 787 - Cheapest Flights Within K Stops
Question
There are n cities connected by some number of flights. You are given an array flights where flights[i] = [fromi, toi, pricei] indicates that there is a flight from city fromi to city toi with cost pricei.
You are also given three integers src, dst, and k, return the cheapest price from src to dst with at most k stops. If there is no such route, return -1.
Example 1:
1
2
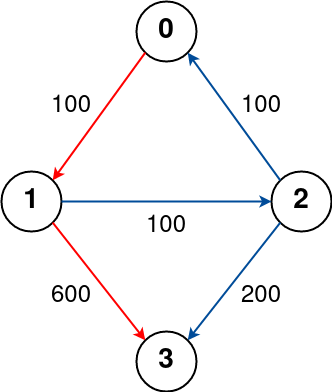
Input: n = 4, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[2,0,100],[1,3,600],[2,3,200]], src = 0, dst = 3, k = 1
Output: 700
Explanation: The graph is shown above. The optimal path with at most 1 stop from city 0 to 3 is marked in red and has cost 100 + 600 = 700. Note that the path through cities [0,1,2,3] is cheaper but is invalid because it uses 2 stops.
Example 2:
1
2
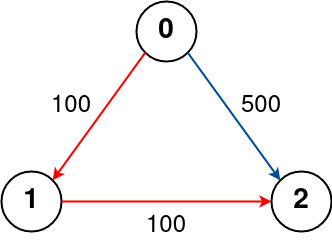
Input: n = 3, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]], src = 0, dst = 2, k = 1
Output: 200
Explanation: The graph is shown above. The optimal path with at most 1 stop from city 0 to 2 is marked in red and has cost 100 + 100 = 200.
Example 3:
1
2
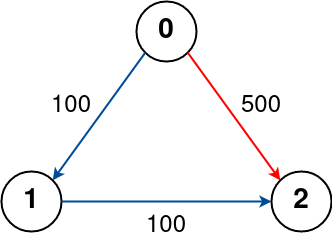
Input: n = 3, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]], src = 0, dst = 2, k = 0
Output: 500
Explanation: The graph is shown above. The optimal path with no stops from city 0 to 2 is marked in red and has cost 500.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 1000 <= flights.length <= (n * (n - 1) / 2)flights[i].length == 30 <= fromi, toi < nfromi != toi1 <= pricei <= 104- There will not be any multiple flights between two cities.
0 <= src, dst, k < nsrc != dst
Links
Question here and solution here
Solution
concept
This question can be solved with Bellman-Ford algorithm which similar to Dijkstra’s algorithm, can find the minimum distance between two nodes. This algo is usually slower but can handle negative edges and also handle restrictions such as maximum of k hopping. The key idea of this algo is to do a BFS-style of traverse on ALL the edges at the same time. Each node’s cost starts at infinity except the starting node, which is 0. We total perform k + 1 iteration (since we can make k jump) iterations, at each iteration:
- we need to make a temp array of the cost such that all updates can be made in this snapshot
- for each edge which is (src, dst, cost), we calculate the cost needed to reach the dst node. (if the src node’s cost is inf, then this edge is skipped)
Why this algo works ? If we have total N node, the shortest edges from starting node to the target node is at most N + 1. For each iteration, we are putting the minimum cost (from the starting node) on each node, and the infinity cost node are the node that cannot be reached in the current iteration. As we iterate through, most node can be reached and its cost is being updated from inf to the actual cost. 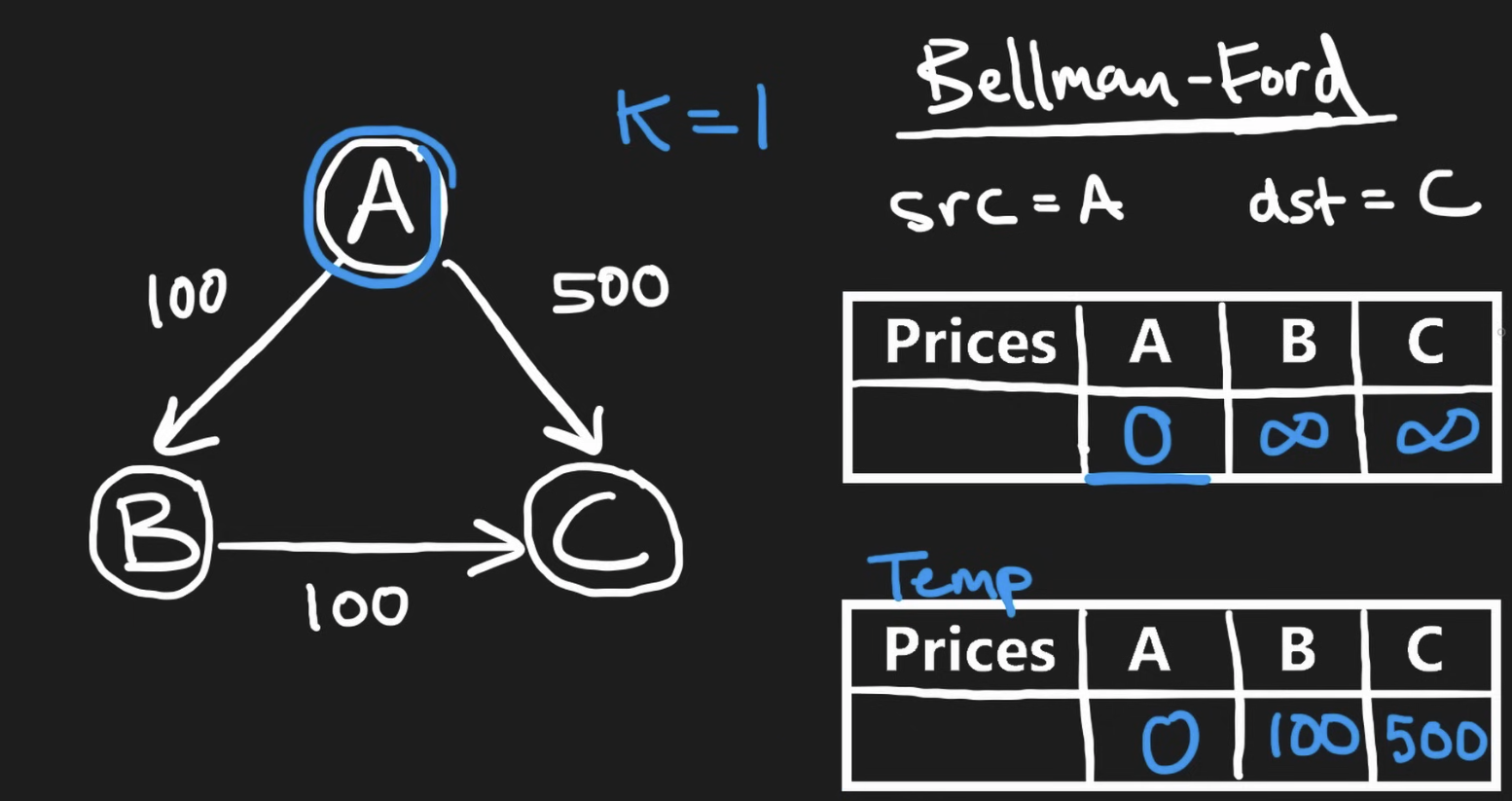
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
class Solution:
def findCheapestPrice(self, n: int, flights: List[List[int]], src: int, dst: int, k: int) -> int:
prices = [float("inf")] * n
prices[src] = 0
for _ in range(k + 1):
tmp_prices = prices.copy()
for source, destination, price in flights:
if prices[source] == float("inf"): # this node is yet reached
continue
if prices[source] + price < tmp_prices[destination]:
tmp_prices[destination] = prices[source] + price
prices = tmp_prices
return -1 if prices[dst] == float("inf") else prices[dst]
Complexity
time: $O((n+m)k)$
space: $O(nk)$
where n is the number of cities, m is the number of flights and k is the number of stops